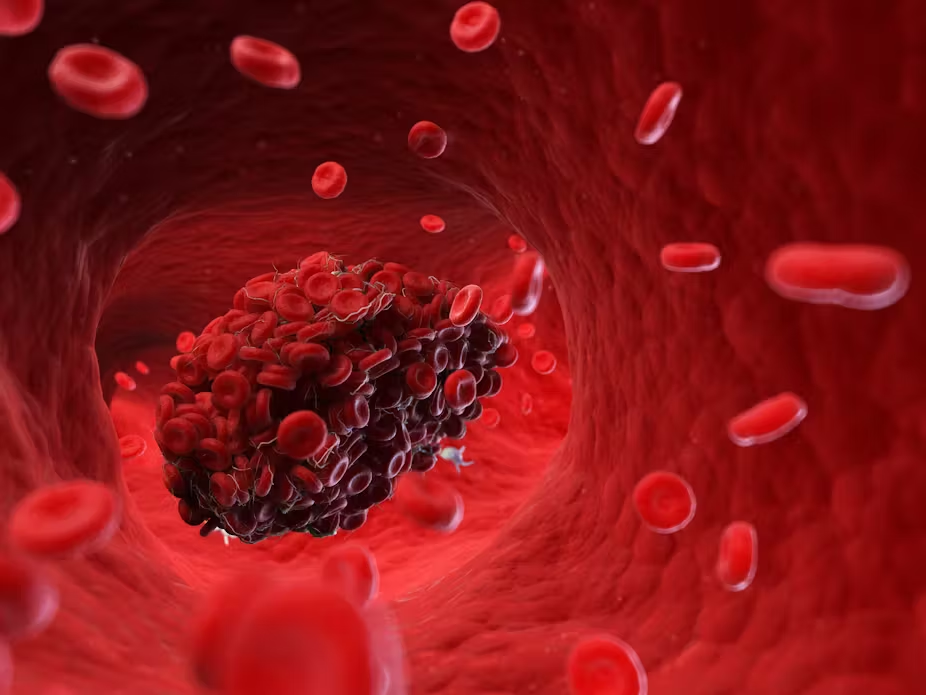
Blood clots can be life-threatening if not addressed quickly. Recognizing the warning signs of a blood clot and knowing when to act can prevent serious complications. In this article, we’ll cover the seven most common signs of a blood clot and offer advice on the next steps to take if you suspect one.
Understanding Blood Clots

Blood clots, medically known as thrombi, are masses of blood that have solidified in your veins or arteries. While clots play an essential role in stopping excessive bleeding when you’re injured, abnormal clots can obstruct blood flow. This leads to conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE), both of which are serious health threats. Recognizing the signs of a blood clot is crucial for getting prompt medical treatment and minimizing risks.
Common Signs of a Blood Clot
Recognizing the signs of a blood clot could save your life or the life of someone you care about. Here are the seven most common signs of a blood clot:
1. Swelling in the Affected Area
One of the most common signs of a blood clot, particularly DVT, is sudden swelling in the affected area—typically a leg or arm. This swelling usually occurs on just one side of the body and is often accompanied by tightness or puffiness in the tissue. The swelling results from blood being blocked by the clot, preventing it from circulating properly.
2. Pain or Tenderness
Pain in the area where the clot has formed is another common symptom. This pain, often described as aching or tenderness, typically begins in the calf or thigh if the clot is in the leg. Some people mistake this for a muscle cramp, but the pain from a blood clot often worsens with time, and it can become more severe when you walk or flex your foot.
3. Red or Discolored Skin
Changes in skin color are another warning sign of a blood clot. The skin over the area may appear red, blue, or purple due to the blockage in blood flow. This discoloration occurs as blood gets trapped in the veins, causing pressure and inflammation. In some cases, the skin may appear shiny or stretched.
4. Warmth in the Affected Area
Warmth in the area where a blood clot has formed is common, particularly in the legs. This warmth is due to the body’s inflammatory response to the clot. The skin may feel noticeably warmer to the touch compared to other areas, and the warmth may be accompanied by tenderness or pain.
5. Sudden Shortness of Breath
If a blood clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism. One of the hallmark symptoms of a pulmonary embolism is sudden shortness of breath. This symptom can come on without warning and may be accompanied by rapid breathing or a feeling of light-headedness. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
6. Chest Pain or Discomfort

Another potential sign of a pulmonary embolism is sharp chest pain that worsens when you take deep breaths or cough. This type of chest pain can sometimes be confused with a heart attack, but it’s often localized and may feel more like stabbing rather than pressure. If you experience chest pain along with shortness of breath, seek emergency medical help right away.
7. Rapid Pulse or Heart Rate
A blood clot can put additional strain on your cardiovascular system, leading to an unusually rapid pulse or heart rate, known as tachycardia. If your heart is beating faster than usual, and this is accompanied by any of the other symptoms mentioned—such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or swelling—this could be a sign that a blood clot is affecting your circulatory system.
What to Do if You Suspect a Blood Clot
If you suspect that you have a blood clot, it’s essential to act quickly. Here’s what you should do:
- Do not massage the affected area: While it may seem tempting to massage or apply pressure to relieve the discomfort, this can be dangerous. Massaging a blood clot can cause it to dislodge and travel to other parts of the body, potentially leading to a pulmonary embolism or stroke.
- Seek immediate medical attention: Contact your doctor or go to the emergency room. Time is of the essence when dealing with a suspected clot, as prompt treatment can prevent further complications.
- Avoid excessive movement: If you suspect a clot in your leg or arm, try to keep the area still while you seek medical help. Excessive movement may increase the risk of the clot traveling to your lungs or heart.
Seeking Medical Attention

Once you’ve sought medical care, doctors will likely perform a physical exam and may use imaging tests like ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs to confirm the presence of a blood clot. Blood tests might also be done to check for clotting disorders or markers of clot formation.
Treatment for blood clots typically includes blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants) to prevent the clot from growing or new clots from forming. In severe cases, surgery or other interventions, such as clot-dissolving medications, may be necessary to remove or break up the clot.
Prevention Measures
Preventing blood clots is a key part of maintaining overall health, especially if you have risk factors such as a family history of clotting disorders, smoking, or prolonged immobility. Here are some measures to help prevent clots:
- Stay active: Regular exercise helps improve circulation and reduce the risk of clots. Even small movements, like stretching your legs during long periods of sitting, can make a difference.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps your blood from thickening, which lowers the risk of clot formation.
- Avoid long periods of immobility: If you’re sitting for extended periods (e.g., during flights or long car rides), make a point to stand up, stretch, and walk around regularly.
- Manage chronic health conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol can increase the risk of clots, so managing these conditions with a healthy lifestyle and medication is crucial.
- Talk to your doctor about medications: If you’re at a higher risk of blood clots, your doctor may prescribe blood thinners or recommend wearing compression stockings to prevent clots from forming.
Conclusion
Blood clots are a medical emergency that require immediate attention. Knowing the signs—such as unexplained swelling, pain, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort—can be life-saving. If you suspect a clot, don’t hesitate to seek medical care. By acting quickly and adopting preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of blood clots and protect your overall health. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and always prioritize your well-being.