Chin hair in women is a surprisingly common concern, yet it’s often surrounded by confusion and misunderstanding. While it might be distressing for some, there’s usually a reason behind it. By understanding the factors contributing to chin hair growth, women can feel more empowered to address it effectively. Let’s explore the primary causes of chin hair in women and what they might indicate about one’s health.
Understanding Chin Hair in Women
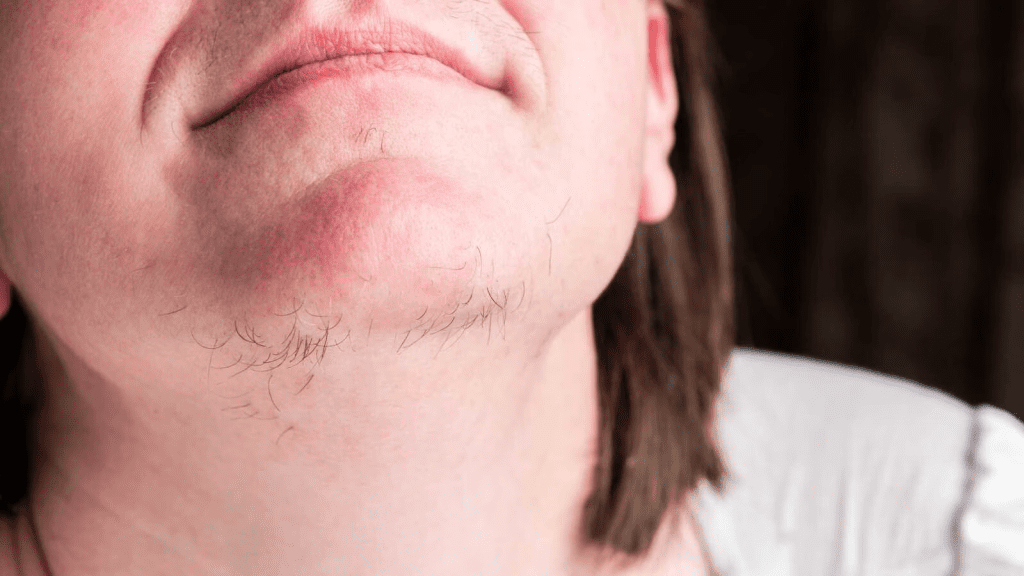
Facial hair on women, especially around the chin, can vary from barely noticeable peach fuzz to thicker, darker strands. For most, this hair is soft and light, but for others, it can become more prominent. This change in hair texture and color can be due to various influences, including genetics, hormonal shifts, and even specific health conditions.
Hormonal Imbalances: A Leading Cause of Chin Hair
Hormones are a major player in the regulation of body hair. Androgens, often labeled as “male hormones,” are present in all women but in much smaller amounts. When there’s an imbalance in these hormones, it can lead to noticeable changes in hair growth, especially on the face and chin.
- High Androgen Levels: Women naturally produce androgens, like testosterone, in small amounts. However, if these levels rise due to an imbalance, it can trigger the growth of coarser, darker hair on the chin.
- Estrogen Decline: During menopause, estrogen levels decrease, which can create a relative increase in androgen levels. This shift often leads to new or increased facial hair growth.
If you’ve noticed a sudden increase in chin hair, it’s a good idea to speak with a healthcare provider, as this can sometimes indicate a hormonal imbalance that may need to be addressed.
The Genetic Influence on Chin Hair Growth
Genetics can play a big role in determining where and how much hair grows on your body, including the chin. If your mother, sisters, or other female relatives have experienced similar facial hair patterns, you may be more prone to it as well.
- Family Traits: Hair growth patterns are often passed down through generations, so if chin hair runs in the family, it’s likely a genetic trait.
- Ethnic Background: Certain ethnic groups may have a higher tendency toward visible facial hair. For instance, women of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and South Asian descent often have a higher likelihood of developing darker, more noticeable facial hair.
While you can’t change your genetics, understanding their role can help you feel more accepting and find methods to manage it effectively.
Health Conditions Linked to Excessive Chin Hair
In some cases, chin hair growth can be a symptom of an underlying health condition. When hair growth is paired with other symptoms, it’s essential to explore potential medical reasons.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
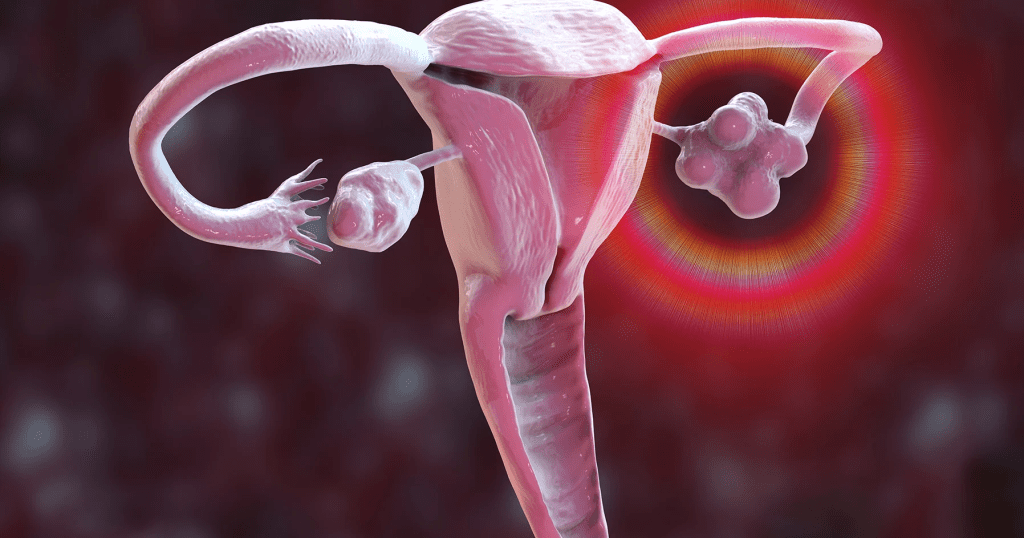
One of the most common causes of excessive facial hair in women is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). This hormonal disorder can result in higher levels of androgens, leading to symptoms such as irregular periods, acne, weight gain, and increased hair growth on the face, particularly the chin.
- Signs of PCOS: Alongside chin hair, symptoms may include missed periods, thinning hair on the scalp, and even skin issues like acne.
- Management: While there’s no cure, symptoms of PCOS can often be managed with lifestyle changes, hormonal treatments, and medications specifically designed to reduce androgen levels.
Adrenal Disorders
Conditions affecting the adrenal glands, such as Cushing’s syndrome, can lead to an overproduction of cortisol and androgens. This hormonal surge can result in increased facial hair growth.
- Symptoms to Watch For: Alongside chin hair, adrenal disorders may cause weight gain, fatigue, high blood pressure, and skin changes.
- Treatment Options: Managing adrenal disorders may involve medication or, in some cases, surgery to address the underlying issue.
Thyroid Imbalances
Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can disrupt the body’s metabolic processes, which in turn, affects hair growth patterns. Thyroid issues may lead to changes in the texture, amount, and distribution of hair on the body, including the chin.
- Associated Symptoms: Hair loss or unusual hair growth, weight fluctuations, mood changes, and temperature sensitivity can all indicate thyroid issues.
- Getting Diagnosed: A simple blood test can often determine if your thyroid function is normal, and treatment can help restore balance.
Medications and Their Unintended Side Effects
Certain medications can lead to unwanted hair growth as a side effect. These include specific steroids, epilepsy treatments, and hormonal medications.
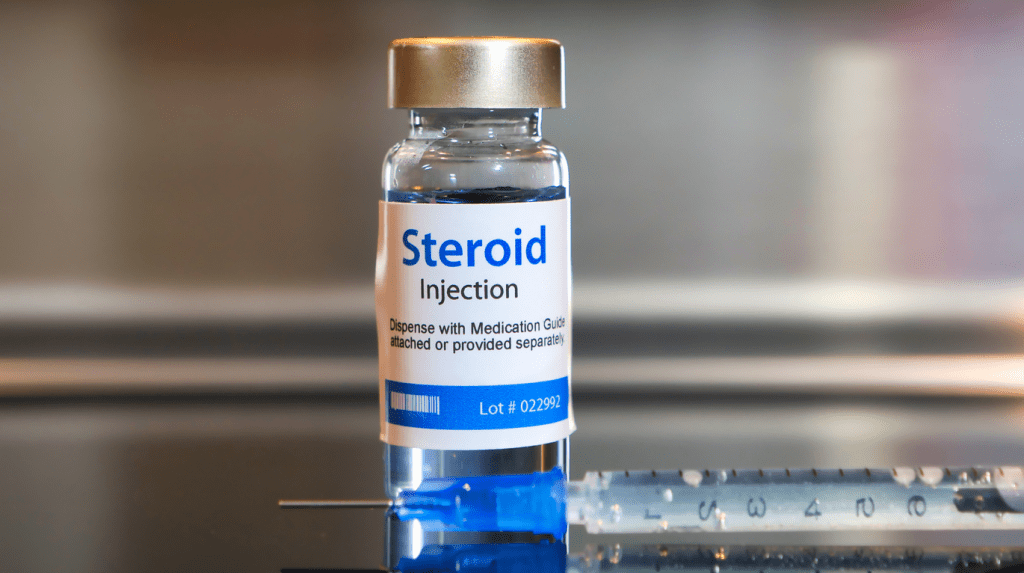
- Steroids: Long-term use of corticosteroids can increase androgen levels, resulting in hirsutism, or excessive body hair growth.
- Hormonal Medications: Medications like testosterone therapy or some contraceptives may lead to increased facial hair, depending on how they interact with your body’s hormonal balance.
If you suspect your medication is causing chin hair growth, it’s worth discussing this with your doctor, who may suggest an alternative treatment.
The Impact of Age and Menopause on Facial Hair
Aging and hormonal shifts during menopause can lead to new or increased facial hair growth in women. As estrogen levels naturally decline with age, the effect of androgens becomes more pronounced, often resulting in chin hair growth.
- Menopausal Changes: Many women experience an uptick in facial hair growth during or after menopause due to decreased estrogen and relative androgen dominance.
- Embracing Change: For many, these changes are a natural part of aging. While it may be bothersome, it’s often manageable with lifestyle adjustments and cosmetic treatments.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Chin Hair

If you’re concerned about chin hair, the first step is consulting with a healthcare provider. They can conduct tests to determine if a medical condition is contributing to your symptoms. Once you know the cause, you can explore treatment options.
- Hormonal Therapies: For conditions like PCOS or thyroid imbalances, hormone regulation can significantly reduce unwanted hair growth.
- Medications: Anti-androgens, such as spironolactone, can help block androgen effects on the body, reducing facial hair.
- Hair Removal Techniques: Options like laser hair removal, electrolysis, and even natural remedies can help manage the appearance of chin hair.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s always a good idea to seek medical advice if you experience sudden or excessive hair growth, especially if accompanied by symptoms like menstrual changes, significant weight gain, or severe acne. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent more serious complications and provide peace of mind.
Conclusion
Chin hair in women is more common than you might think, and it can result from various factors, including hormonal imbalances, genetics, and health conditions like PCOS or thyroid disorders. By understanding these underlying causes, you can take steps to manage and treat chin hair effectively. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical treatments, or hair removal techniques, there are ways to address this issue and feel more comfortable in your skin. If you’re concerned, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional to explore the best options for your individual needs.


